Molecules, Free Full-Text
4.5 (110) In stock
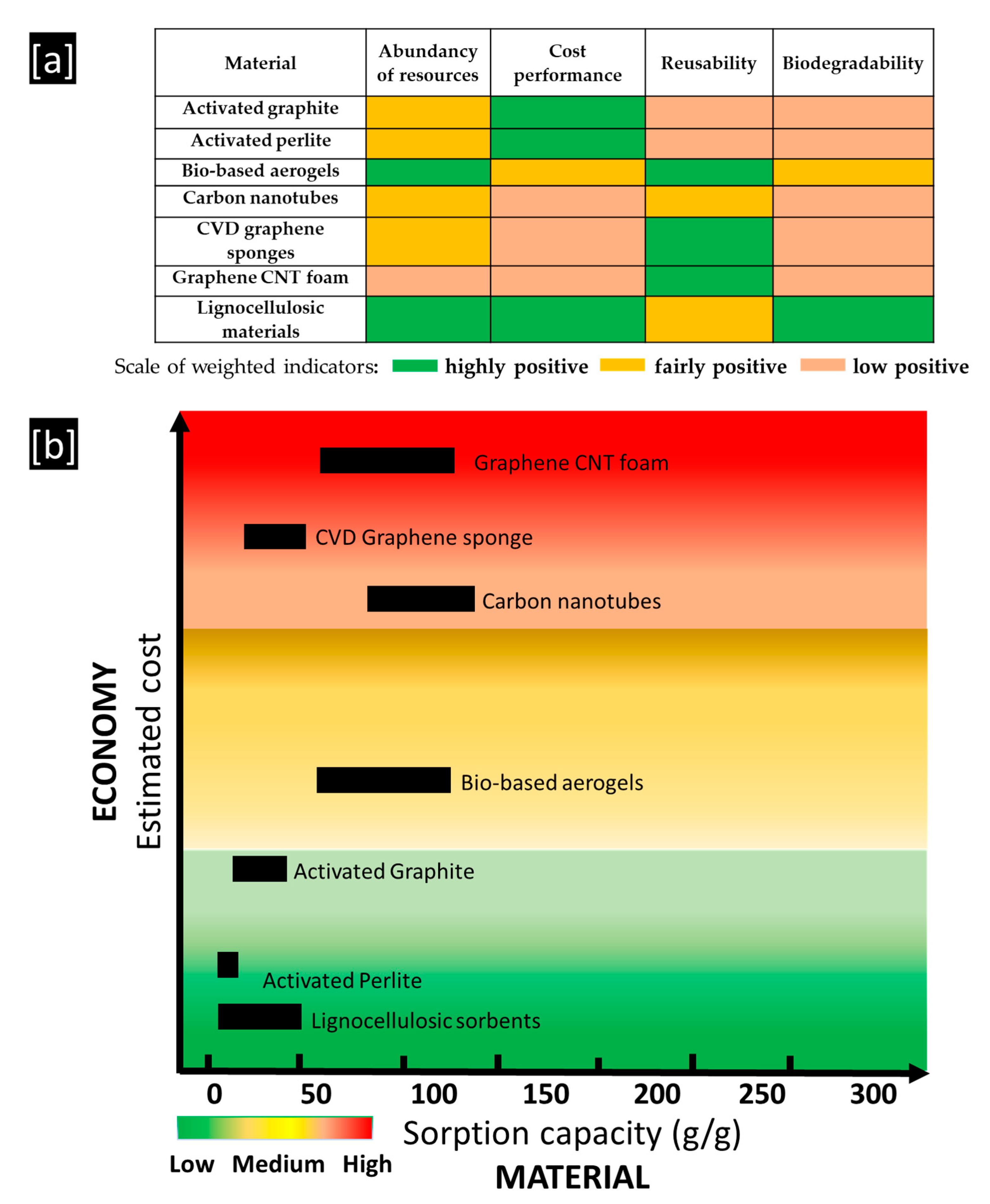
Conventional synthetic sorbents for oil spill removal are the most widely applied materials, although they are not the optimal choices from an economic and environmental point of view. The use of inexpensive, abundant, non-toxic, biodegradable, and reusable lignocellulosic materials might be an alternative to conventional sorbents, with obvious positive impact on sustainability and circular economy. The objective of this paper was to review reports on the use of natural-based adsorbing materials for the restoration of water bodies threatened by oil spills. The use of raw and modified natural sorbents as a restoration tool, their sorption capacity, along with the individual results in conditions that have been implemented, were examined in detail. Modification methods for improving the hydrophobicity of natural sorbents were also extensively highlighted. Furthermore, an attempt was made to assess the advantages and limitations of each natural sorbent since one material is unlikely to encompass all potential oil spill scenarios. Finally, an evaluation was conducted in order to outline an integrated approach based on the terms of material–environment–economy.
Molecules, Free Full-Text, mate pastor con negras
Molecules, Free Full-Text
Molecules, Free Full-Text, fluorescent
Molecule Images, HD Pictures For Free Vectors Download
Molinspiration Cheminformatics

Molecules An Open Access Journal from MDPI
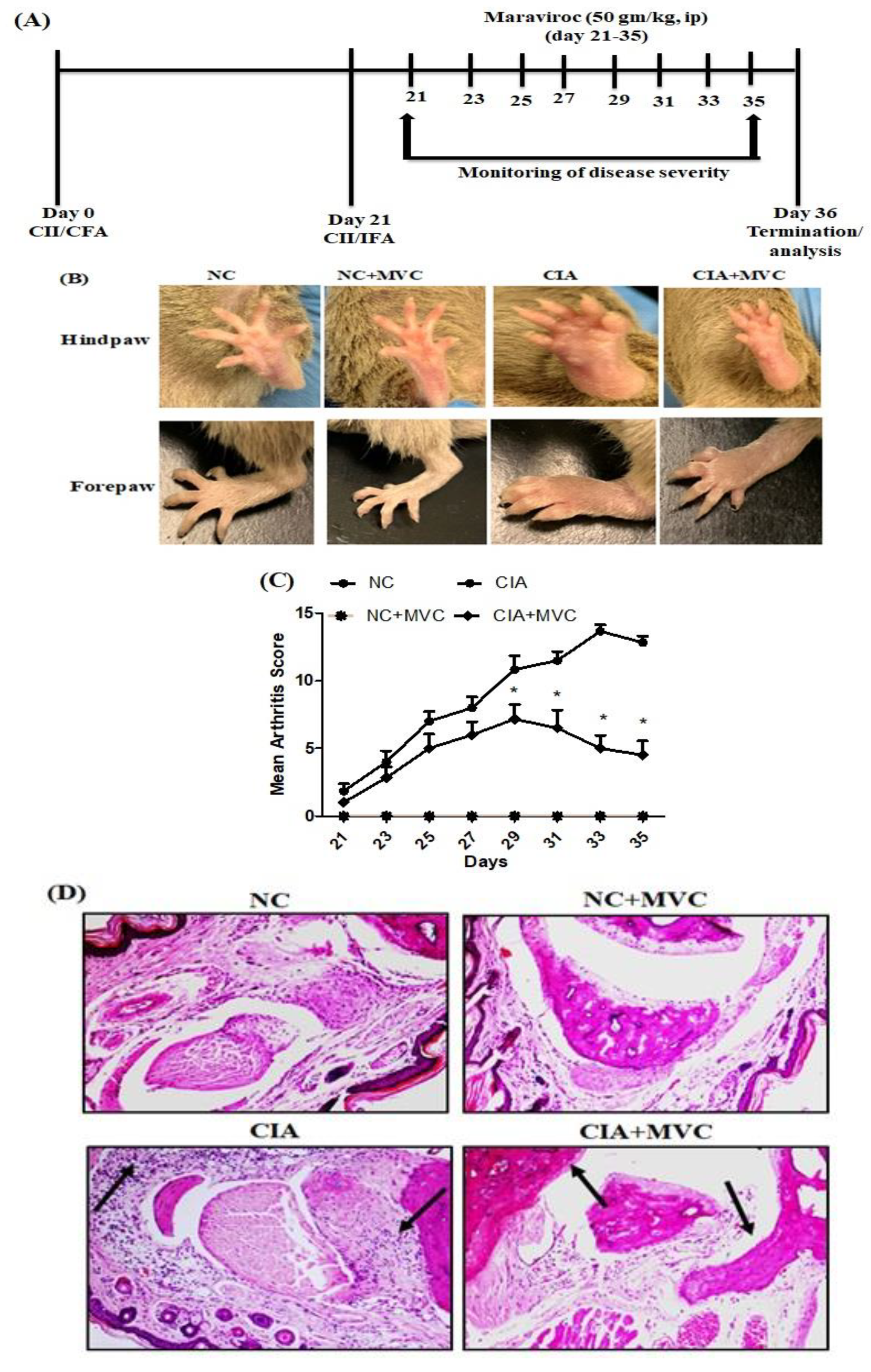
Molecules, Free Full-Text, mdpope 3

Molecule Pictures Download Free Images on Unsplash

A to Z Index
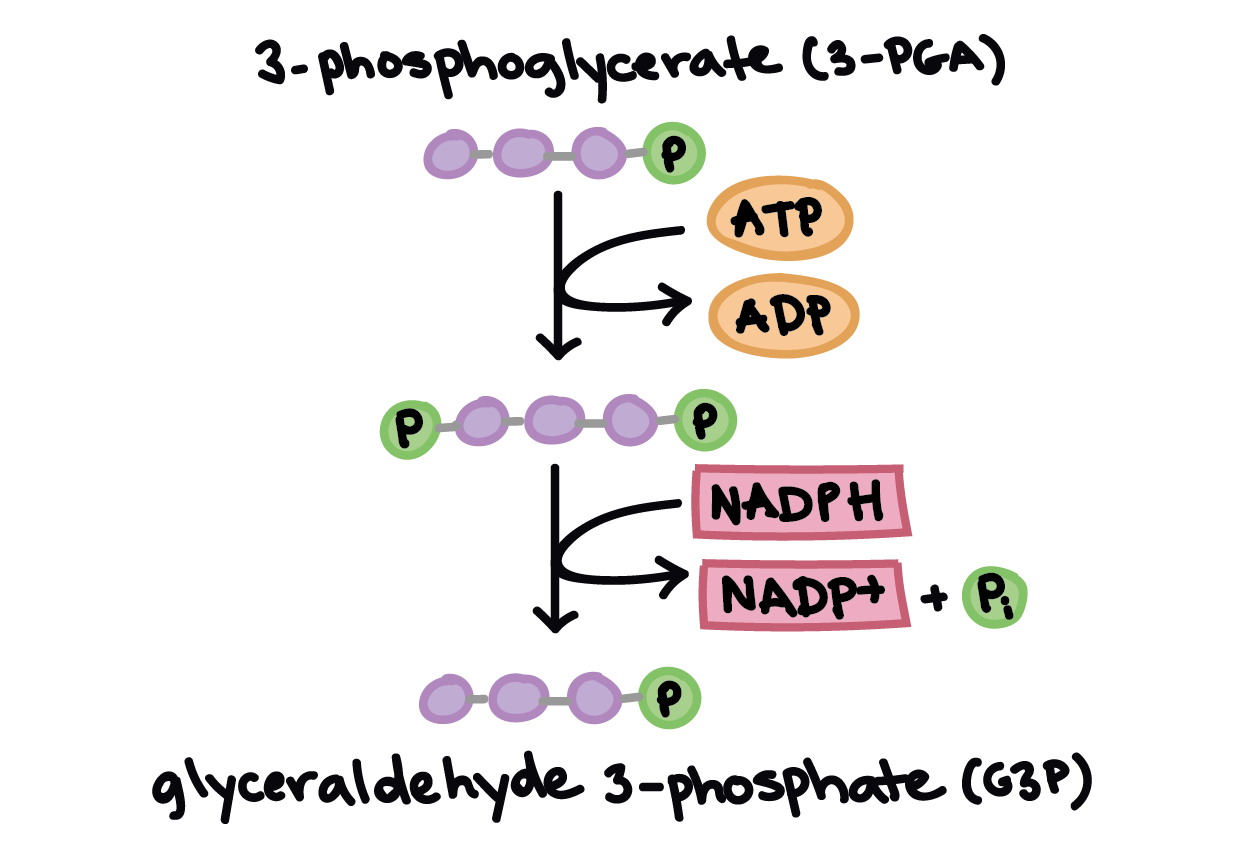
The Calvin cycle (article), Photosynthesis

Molecules, Free Full-Text, onoo 2
Benchmark information for CORE-OM.
Manuals EORTC – Quality of Life
 NWT Triumph 'Contouring Sensation W01' Underwired Minimiser Bra Black Nude 36G
NWT Triumph 'Contouring Sensation W01' Underwired Minimiser Bra Black Nude 36G How to Set Up a Perfect Creator Laptop Workstation
How to Set Up a Perfect Creator Laptop Workstation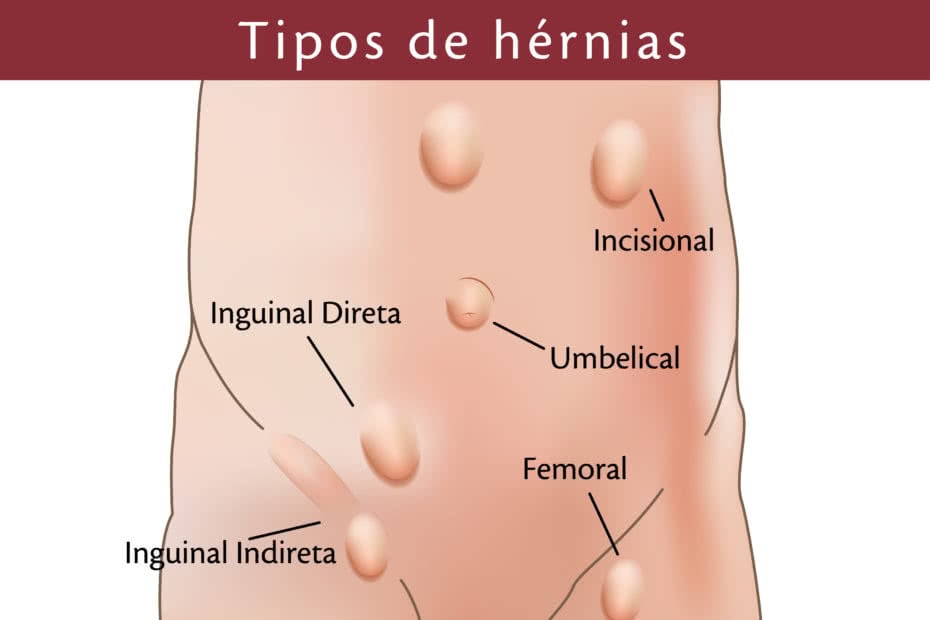 tipos de hérnia Descubra tudo sobre hérnias: umbilical, inguinal
tipos de hérnia Descubra tudo sobre hérnias: umbilical, inguinal Undercover UC1011 - Classic 99-06 (07 Classic) Silv/Sierra 8' SRW
Undercover UC1011 - Classic 99-06 (07 Classic) Silv/Sierra 8' SRW Soft Touch Skin Shiner Lemon Enriched 500ml – Al Ghafoor Centre
Soft Touch Skin Shiner Lemon Enriched 500ml – Al Ghafoor Centre adidas Girls' Allover Print 3-Stripes Tights, Charcoal Grey Heather, M (10/12)
adidas Girls' Allover Print 3-Stripes Tights, Charcoal Grey Heather, M (10/12)