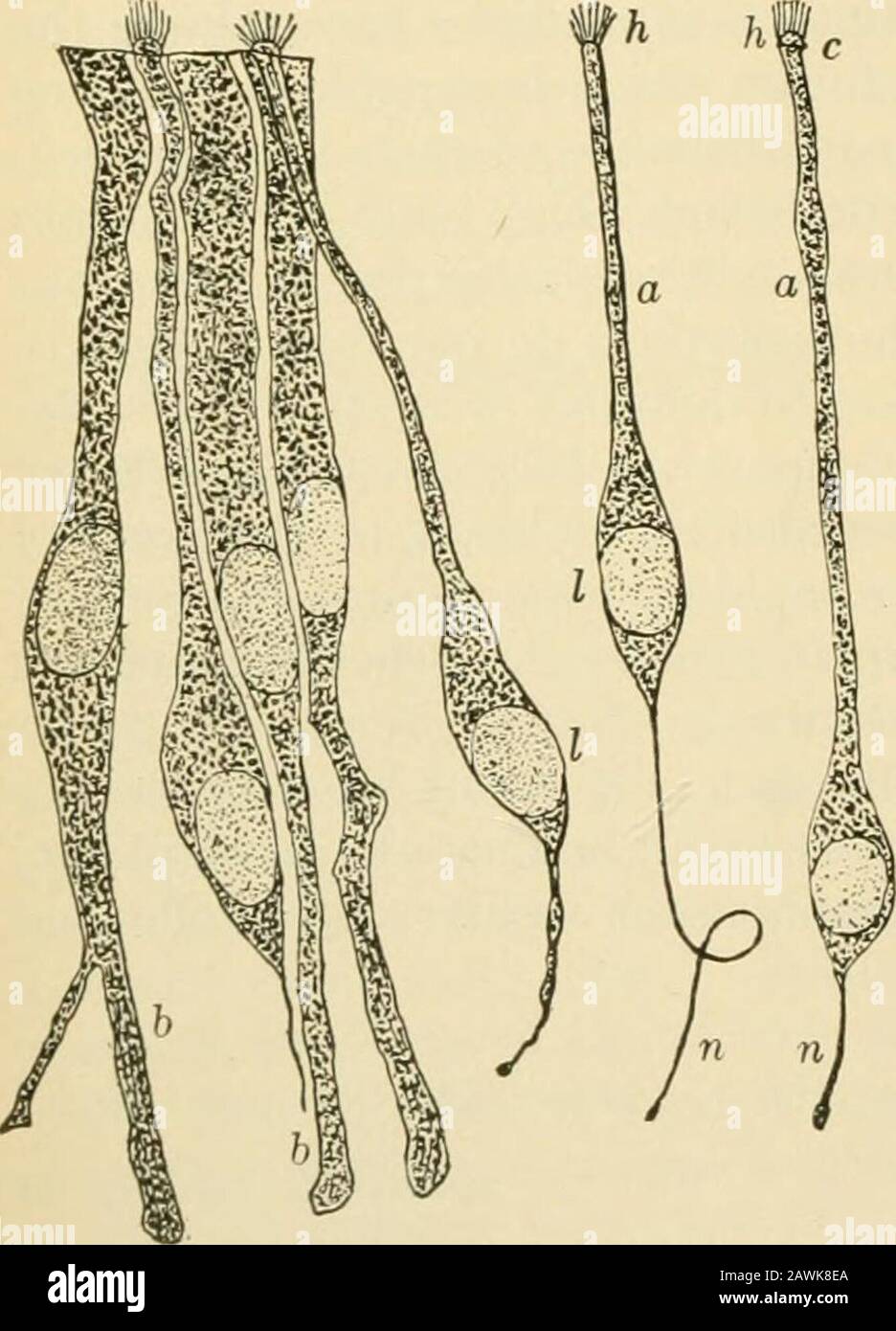
Nature and development of plants . The basal portion of the sporo-phyte develops into a massive foot, often provided with rhizoidal-like outgrowths, which serve as a very efficient absorbing organ.The upper portions
4.8 (775) In stock
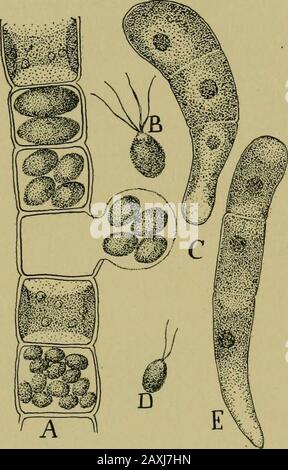
Download this stock image: Nature and development of plants . The basal portion of the sporo-phyte develops into a massive foot, often provided with rhizoidal-like outgrowths, which serve as a very efficient absorbing organ.The upper portions of the sporophyte present a remarkableseries of differentiations. The outer part of it consists of chloro-phyll-bearing cells in which, for the first time, genuine stomataappear (Fig. 199, ch). Within this zone of chlorenchyma is adome-shaped layer of spore mother cells alternating with sterilecells which in some genera develop as elaters. In the center ofthe sporophyte is a mass o - 2AXH45J from Alamy's library of millions of high resolution stock photos, illustrations and vectors.
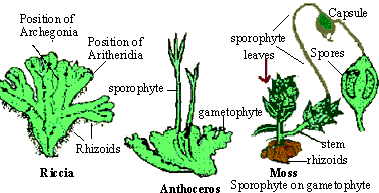
Biology Study Guide - 14.3 Kingdom : Plantae

Dictionary of Plant Biology En-Sp, PDF, Adenosine Diphosphate
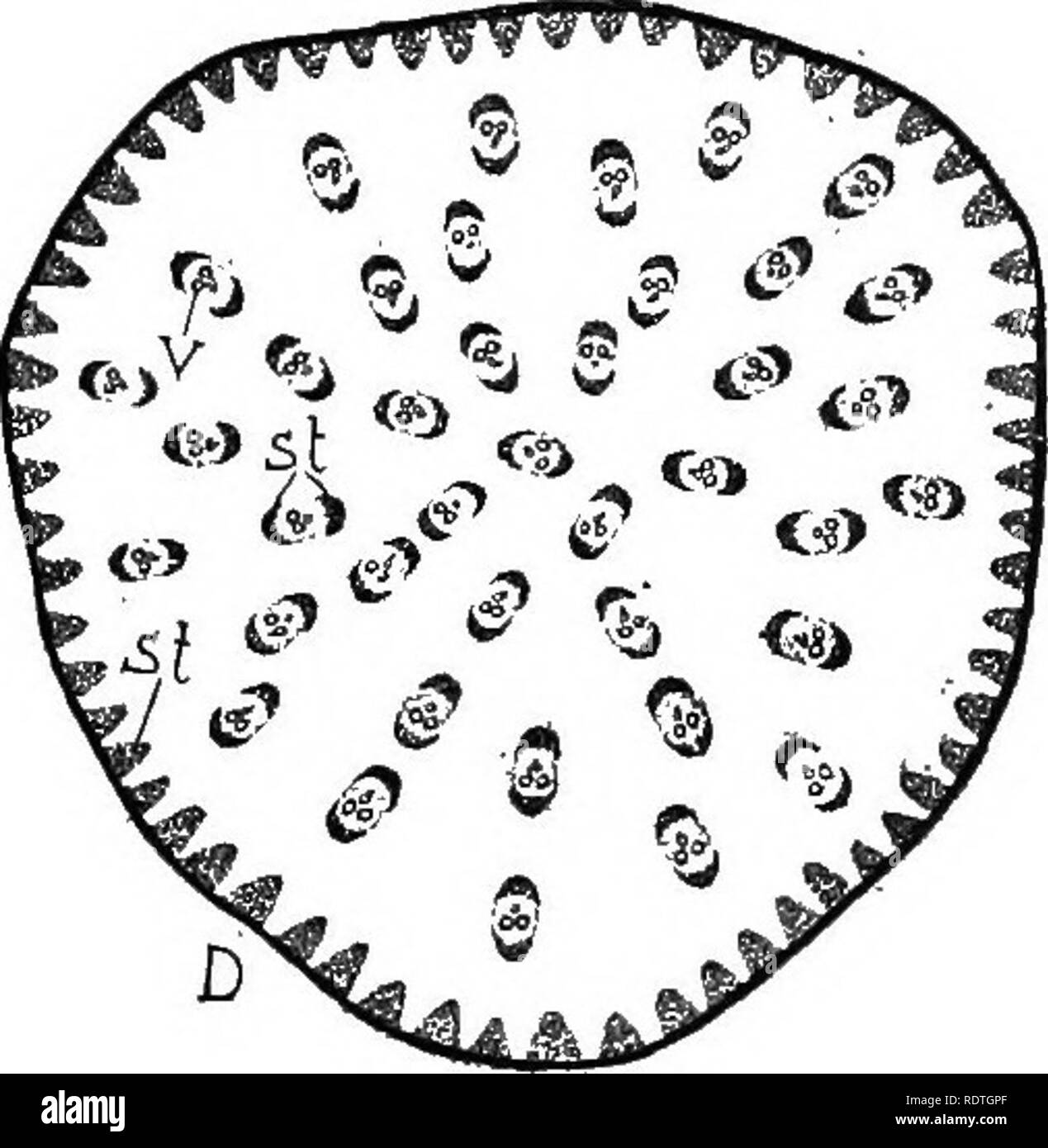
Natur und Entwicklung von Pflanzen . Der basale Teil des Sporophyten entwickelt sich zu einem massiven Fuß, der oft mit rhizoidartigen Auswüchsen versehen ist, die als sehr effizientes absorbierendes Organ dienen.Die oberen
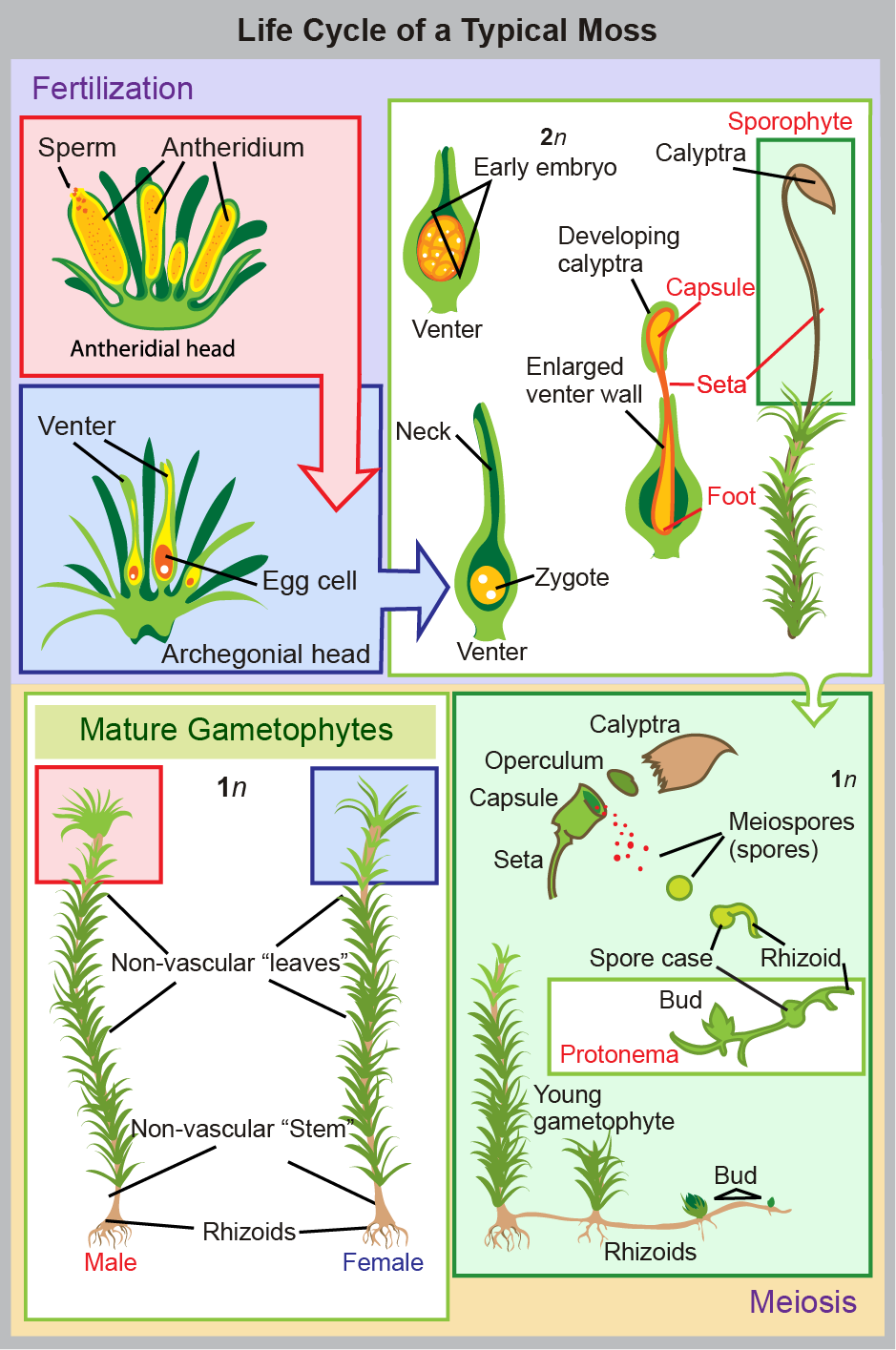
4. Bryophytes, the Bryophyte Lifecycle, and Adaptations - LabXchange

Biology Chapter Notes, PDF, Ion
Basal layer hi-res stock photography and images - Page 3 - Alamy

Foot, plant organ

The Project Gutenberg eBook of Elementary Botany, by George Francis Atkinson
Course: Biology
Thalassiosira sinica, LM. Fig. 1. Single cells. Fig. 2. Valve view
Algae - Definition, Types, Reproduction, Size & Form - Biology
 Olive Crash Cross Tights
Olive Crash Cross Tights Susan Graver Women's Weekend Petite Solid & Printed Premium Stretch Sl – Smarams
Susan Graver Women's Weekend Petite Solid & Printed Premium Stretch Sl – Smarams Toeless Half Palm Yoga Socks Toe Protection Sweat absorbing - Temu
Toeless Half Palm Yoga Socks Toe Protection Sweat absorbing - Temu FREE PEOPLE Sanctuary Sports Bra White Ruffle
FREE PEOPLE Sanctuary Sports Bra White Ruffle blonde with flirtatious look. flirting girl. flirt concept. Stock Photo
blonde with flirtatious look. flirting girl. flirt concept. Stock Photo No27 Mens Navy Blue Whale on Gray Leather Belt,Nautical Whale Ribbon and webbing style belt, Brass Buckles : Clothing, Shoes & Jewelry
No27 Mens Navy Blue Whale on Gray Leather Belt,Nautical Whale Ribbon and webbing style belt, Brass Buckles : Clothing, Shoes & Jewelry